The Cash Conversion Cycle Explained
From Purchase to Payment: Mastering the Cash Conversion Cycle for Business Growth.
Introduction
The cash conversion cycle (CCC) may sound like a complex financial term, but it holds the key to understanding how efficiently your business transforms its investments into cash. In a world where ‘cash is king,’ comprehending how this cycle functions can be a game-changer for your organization. Whether you’re a small business owner, an investor, or a finance enthusiast, this in-depth guide will unravel the mystery of the cash conversion cycle and the vital role of cash on hand. So, buckle up and dive into the financial concept that could revolutionize your approach to managing money.
A business’s financial ecosystem is like a well-designed machine’s intricate workings. Each part must function in harmony with the others to achieve optimal performance. One of the critical mechanisms within this financial machine is the cash conversion cycle. Ignoring it could lead to missed opportunities, while understanding and optimizing it could unlock unprecedented growth.
As we delve into the details, you’ll discover the cash conversion cycle, why it matters, how to calculate it, and the strategies to improve it. With insights on maintaining adequate cash, this guide will provide you with actionable knowledge to navigate the financial waters of today’s dynamic business landscape.
What is the Cash Conversion Cycle?
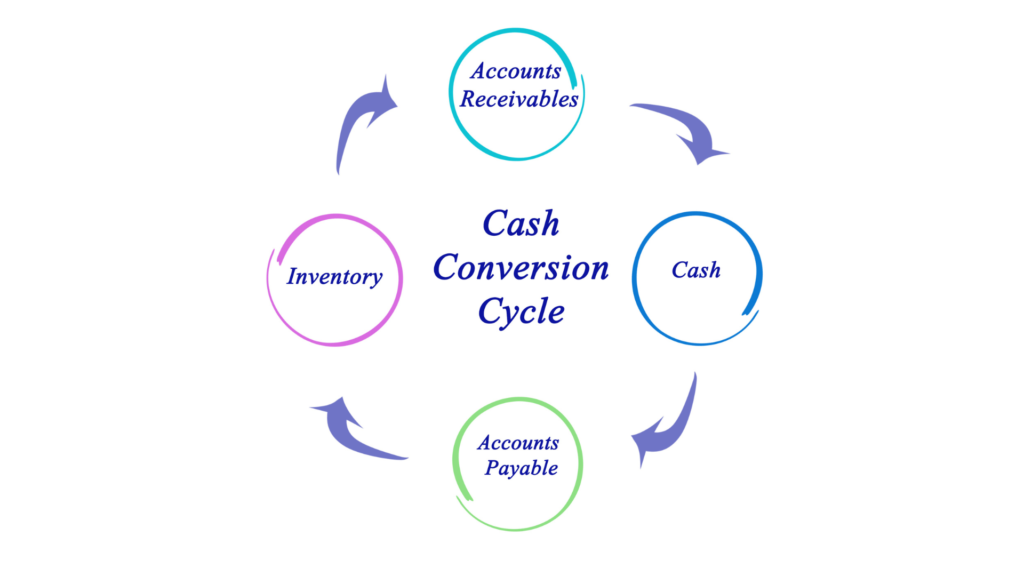
Definition
The Cash Conversion Cycle (CCC) is a vital metric in business operations. It quantifies the time a company takes to convert its inventory and other resources into cash from sales.
Components:
- Inventory Period: How long it takes to sell inventory.
- Accounts Receivable Period: The time required to collect payment for sales.
- Accounts Payable Period: The period to pay suppliers.
Each of these stages plays a significant role in the efficiency and liquidity of a business.
Importance of CCC
The CCC tells a story about how efficiently a company manages its working capital. A shorter CCC shows a quicker conversion of investments into cash, which can be used for growth and other possibilities. In difference, a longer CCC may signal inefficiency, potentially putting strain on the business’s cash on hand.
Detailed Examination of the Cash Conversion Cycle
Inventory Period
Overview
The inventory period begins when you acquire inventory and ends when you sell it. The shorter this period, the less money is tied up in stock, enhancing liquidity.
Factors Affecting Inventory Period
- Supply Chain Efficiency: Delays in supply can prolong the inventory period.
- Market Demand: High demand can shorten the inventory period, while low demand can extend it.
- Inventory Management System: Automated systems can optimize stock levels, lowering the period.
Accounts Receivable Period
Overview
This period represents the time it takes to collect payment for sales. The quicker you can collect payment, the better your cash flow.
Factors Affecting Accounts Receivable Period
- Payment Terms: Shorter credit terms can reduce the receivable period.
- Customer Payment Behavior: Late payments from customers can prolong the period.
- Invoice Accuracy: Accurate and precise invoicing can expedite payment.
Accounts Payable Period
Overview
The accounts payable period is the time you take to pay your suppliers. A longer accounts payable period might provide more flexibility with cash on hand.
Factors Affecting Accounts Payable Period
- Supplier Payment Terms: Longer credit periods from suppliers can extend the payable period.
- Cash Management Strategy: Timing payments to align with cash inflow can manage the payable period efficiently.
Calculating the Cash Conversion Cycle
The CCC is calculated using the following formula:
CCC = Inventory Conversion Period + Receivables Conversion Period – Payables Conversion Period.
Cash on Hand: An Essential Part of Business Operations
Definition
Cash on hand refers to the money readily available to a business. It’s the immediate liquidity used for various costs and opportunities.
Importance
- Meeting Immediate Obligations: Bills, salaries, and unexpected expenses.
- Investing in Opportunities: Capitalizing on new business experiences.
- Providing Stability: Acting as a financial cushion during downturns.
Strategies to Enhance Cash Conversion Cycle
Optimize Inventory Management
- Implement JIT (Just-in-Time) Method: Reduces holding costs.
- Utilize Technology: Automate ordering to align with demand.
- Regular Monitoring: Regularly review inventory levels.
Accelerate Receivables Collection
- Clear Payment Terms: Ensuring customers understand when payments are due.
- Early Payment Incentives: Offering discounts for early payments.
- Regular Follow-ups: Consistent communication with customers about outstanding payments.
Negotiate Favorable Payment Terms with Suppliers
- Build Strong Relationships: Work closely with suppliers to negotiate mutually beneficial terms.
- Utilize Trade Credit: Take advantage of credit offered by suppliers.
- Pay on Time: Establish a history of timely payments to enhance negotiation leverage.
Industry-Specific Considerations for Cash Conversion Cycle
Different industries face unique challenges in managing the CCC. A strategic approach tailored to each sector is essential for success.
Technology Sector

Different industries face unique challenges in managing the CCC. A strategic approach tailored to each sector is essential for success.
Here are three examples of how technology companies can optimize their CCC
- Implementing Automated Inventory Management – Example: Dell:
- Problem: Dell faced challenges with overstocking and understocking components for its customizable computers, impacting its CCC.
- Solution: By implementing a Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory system, Dell began building computers based on real-time orders rather than forecasts. This minimized holding costs and reduced the time inventory sat in warehouses.
- Outcome: Dell’s transition to JIT inventory management significantly reduced the Inventory Conversion Period (ICP), thus shortening the overall CCC. It increased cash on hand, allowing Dell to be more responsive to market demands.
- Utilizing Artificial Intelligence in Receivables Collection – Example: IBM:
- Problem: IBM’s varied client base and global reach led to complex receivables management, affecting the Receivables Conversion Period (RCP).
- Solution: IBM deployed artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze customer payment patterns, predict potential delays, and identify optimal collection strategies.
- Outcome: By leveraging AI, IBM reduced its RCP by promptly identifying and acting on delayed payments. It improved cash flow and allowed for better customer relationship management by tailoring collection approaches based on individual behavior.
- Enhancing Supplier Negotiation through Data Analytics – Example: Apple:
- Problem: Apple’s extensive global supply chain led to challenges in managing the Payables Conversion Period (PCP) with various suppliers, impacting the CCC.
- Solution: Apple utilized data analytics to gain insights into supplier performance, cost structures, and market conditions. By analyzing this data, Apple could negotiate favorable payment terms without risking supplier relationships.
- Outcome: By strategically extending or reducing the PCP through informed negotiations, Apple optimized its CCC to align with its overall cash flow goals and seasonal product launch needs.
These examples demonstrate that by embracing technology and data-driven approaches, tech companies can enhance their CCC through inventory management, receivables collection, and supplier negotiations. This multifaceted optimization strengthens financial stability and enhances adaptability and responsiveness to market dynamics.
Healthcare

- Regulatory Compliance: Strict regulations affect inventory and payment terms.
- Patient Care Considerations: Balancing financial efficiency with patient needs.
- Insurance and Billing Complexities: Navigating various payment structures and timelines.
Here are three examples of how healthcare companies can enhance their CCC:
1. Streamlining Patient Billing Processes – Example: Mayo Clinic:
- Problem: Mayo Clinic struggled with delays in receivables due to convoluted billing processes, affecting the Receivables Conversion Period (RCP).
- Solution: Mayo Clinic implemented a transparent and automated billing system that promptly communicated charges to patients and insurance providers. They also integrated an easy-to-understand billing statement to minimize confusion.
- Outcome: The new streamlined billing process reduced the time to collect payments from patients and insurers, shortening the RCP and improving the overall CCC. It also enhanced patient satisfaction and trust in the billing process.
2. Optimizing Inventory Management for Medical Supplies – Example: Johnson & Johnson:
- Problem: Johnson & Johnson found inefficiencies in its inventory management system, leading to excess stock or shortages of critical medical supplies, thus affecting the Inventory Conversion Period (ICP).
- Solution: They implemented a real-time inventory tracking system, enabling them to match supply with demand closely. This allowed for better supplier coordination, reducing holding costs, and mitigating stockouts.
- Outcome: By optimizing inventory levels, Johnson & Johnson significantly reduced the ICP, positively affecting the CCC, ensuring product availability, and reducing costs tied to excess inventory.
3. Leveraging Data Analytics in Payables Management – Example: Cleveland Clinic:
- Problem: Cleveland Clinic faced challenges in managing its Payables Conversion Period (PCP) due to varying payment terms across numerous suppliers.
- Solution: Cleveland Clinic utilized data analytics to analyze supplier performance and payment terms. This analysis enabled them to negotiate favorable payment terms strategically, considering supplier reliability, bulk discounts, and market conditions.
- Outcome: By effectively managing the PCP through data-driven decisions, Cleveland Clinic could extend favorable payment terms without straining supplier relationships. This allowed them to keep more cash on hand while ensuring supply chain stability.
These healthcare examples illustrate that enhancing the CCC is attainable through a focus on streamlining billing processes, optimizing inventory management, and employing data analytics in supplier negotiations. Such strategies contribute not only to financial health but also to the efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare delivery. By maintaining an optimized CCC, healthcare organizations can ensure they have the necessary financial resources to continue innovating and providing high-quality care.
E-Commerce

- Multichannel Sales: Managing inventory across online platforms.
- Customer Expectations: Providing fast shipping without overstocking.
- Seasonal Trends: Adapting to changes in consumer behavior during different seasons.
Here are three examples of how e-commerce companies can enhance their CCC:
1. Automating Order Fulfillment and Inventory Management – Example: Amazon:
- Problem: With millions of products, Amazon faced challenges tracking inventory and promptly fulfilling orders, extending the Inventory Conversion Period (ICP).
- Solution: Amazon implemented cutting-edge automation in their warehouses and integrated AI-powered inventory management. This allowed them to process orders quickly, minimize holding times, and predict inventory needs more accurately.
- Outcome: By automating order fulfillment and optimizing inventory, Amazon reduced the ICP significantly. This has contributed to their ability to offer fast shipping times and maintain customer satisfaction while decreasing costs.
2. Enhancing Payment Collection with One-Click Checkout – Example: Shopify:
- Problem: Shopify recognized that complicated checkout processes led to shopping cart abandonment and delays in collecting payment, affecting the Receivables Conversion Period (RCP).
- Solution: Shopify introduced a one-click checkout option for returning customers, storing payment information securely and allowing quicker completion of purchases.
- Outcome: This simple yet effective innovation reduced the RCP by facilitating immediate payment, lowering abandonment rates, and improving the overall CCC. Customers enjoyed a seamless shopping experience, leading to repeat business.
3. Strategically Managing Supplier Relationships – Example: Zalando:
- Problem: Zalando, a fashion e-commerce company, struggled with inconsistent supplier relationships, leading to fluctuating payment terms and affecting the Payables Conversion Period (PCP).
- Solution: Zalando initiated a strategic supplier management program, building strong relationships with key suppliers and negotiating favorable payment terms based on purchase volumes, reliability, and timing.
- Outcome: By aligning payment terms with the company’s cash flow needs, Zalando was able to optimize its PCP. This approach maintained supplier trust and allowed Zalando to have more cash on hand when needed, enhancing their overall CCC.
These examples from the e-commerce sector show that focusing on the three main components of the CCC – Inventory Conversion Period (ICP), Receivables Conversion Period (RCP), and Payables Conversion Period (PCP) – can lead to significant enhancements in cash management. Whether through technological innovation, customer experience enhancement, or supplier relationship management, e-commerce companies can find tailored strategies to improve their CCC and strengthen their financial position.
Construction

- Long Project Timelines: Managing cash flow over extended periods.
- Substantial Upfront Costs: Significant initial investment in materials and labor.
- Contract Payment Terms: Navigating complex contractual payment structures.
Here are three examples of how construction companies can enhance their CCC:
1. Utilizing Construction Management Software – Example: Turner Construction Company:
- Problem: Managing numerous projects and suppliers led to delays in billing, approval, and payment, affecting both the Receivables Conversion Period (RCP) and Payables Conversion Period (PCP).
- Solution: Turner Construction Company adopted construction management software that streamlined their entire workflow – from procurement to project completion. This included tracking supplier deliveries, automating invoice approval, and scheduling payments.
- Outcome: By implementing this software, Turner significantly reduced the time to process invoices and receive payments. This improved RCP and PCP, enhancing the overall CCC and increasing liquidity.
2. Implementing Just-In-Time (JIT) Inventory Management – Example: Skanska:
- Problem: Holding excess inventory for various projects was tying up cash and extending the Inventory Conversion Period (ICP).
- Solution: Skanska implemented a JIT inventory management system, coordinating with suppliers to deliver materials only as needed. This approach was supported by robust demand forecasting and communication with suppliers.
- Outcome: Skanska reduced the holding costs and the amount of tied-up capital in inventory, thus reducing the ICP and improving the overall CCC. The approach also minimizes waste and storage costs.
3. Improving Payment Terms with Performance Incentives – Example: Bechtel Corporation:
- Problem: Bechtel faced challenges with extended payment terms from clients and the subsequent effect on the Receivables Conversion Period (RCP).
- Solution: Bechtel introduced performance-based incentives in their contracts, where clients would benefit from discounted rates or other advantages if they adhered to preferred payment schedules.
- Outcome: This innovative contract approach encouraged clients to pay sooner, improving Bechtel’s RCP. It fostered better client relationships and allowed more predictable cash flow management, enhancing the overall CCC.
Enhancing the Cash Conversion Cycle in the construction industry often requires innovative approaches to project management, supplier relationships, and contract structuring. By focusing on these critical areas, construction companies like Turner Construction, Skanska, and Bechtel have substantially improved their CCC, leading to more robust financial management and the ability to invest in growth opportunities.
The Future of Cash Management
Trends
- Automation: Integrating AI and machine learning to predict and manage cash flow.
- Real-Time Analytics: Utilizing data for immediate insights.
- Integration Across Platforms: Seamless data flow between inventory, sales, and accounting systems
Innovations
- Blockchain: Secure and transparent transactions.
- Predictive Analysis: Using AI to anticipate future cash flow needs and market trends.
Conclusion
The cash conversion cycle is a multifaceted, vital aspect of business operations. It’s a key indicator of efficiency and financial health, directly impacting the cash. By understanding and optimizing the CCC, businesses can enhance liquidity, embrace growth opportunities, and build a resilient financial foundation. The utilization of technology and alignment with industry-specific trends can further refine this process, ensuring future success. Whether a startup or an established enterprise, the principles and strategies discussed provide a roadmap to achieving financial success through effective cash management.
Ready to dive deeper into managing your Accounts Receivable? Contact us today to explore how you can make AR work for your business.
